│Exercise Scheduling│ER Organization│Organization Chart│Back│
Emergency Response (ER)
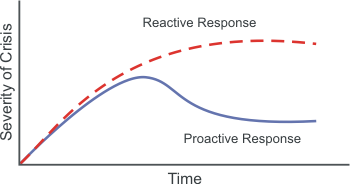
In case of accident, to take action to prevent to be a crisis The Impact of Proactive vs. Reactive Forces
- Incident
- Incident can occur fairly regularly and often do not escalate to the point of an emergency or crisis.
- Each incident should be mitigated as quickly as possible and monitored and evaluated to ensure that it does not escalate to crisis.
- Additionally, an incident can serve to identify prevention efforts which could decrease the likelihood of the incident occurring again.
- Emergency
- Immediate effects are often local in nature (i.e., on site fire; pipe burst with oil spilling into containment dikes; or computer malfunction)
- Impacts typically are short-term (i.e., minor loss in production time; minimal air pollution due to fire smoke)
- On-site local area resources are generally adequate to respond to and manage the situation
- May or may not have potential to escalate into a crisis
- Timeframe for action is extremely limited
- Limited and often conflicting information regarding the situation,
- Crisis
- Potential to impact the organization with long-term consequences
- May require significant corporate resources (financial support, staffing management and technical expertise, etc.) to respond effectively
- Off-site and contract resources are usually required
- Timeframe for action is extremely limited
- Limited and often conflicting information regarding the situation
- Disaster
- Disasters are thought of in terms of natural disasters and the consequence of these events on a specific geographic area.
- Disaster example include the flooding, earthquake, etc.
- Emergency Management
- The focus of emergency management tends to be tactical; i.e. to “put out the fire” and manage all the activities associated with that task.
- Notification of response personnel that an incident has occurred
- Managing emergency resources and response activities at the site (i.e. fire brigade, evacuation teams, etc.)
- Ensuring that any and all necessary equipment is either in place or on way to the site
- Crisis Management
- Crisis management encompasses tasks associated with overseeing the management of emergency response, but it focuses on the consequences and strategic aspects or impacts of the incident.
- A crisis team usually has oversight authority with regard to the emergency management efforts.
- The strategic and long-term consequences of the incident should be the main focus of a crisis management team. In the fire example used above, the crisis team should be considering such issues as:
- The impact of image, and the need/parameters of humanitarian or claims efforts for the surrounding community
- The impact of the crisis on a pending contract to build a similar facility in the town 10 miles away
- Other long-term business consequences that may arise from an emergency or other circumstances
- Exercise make Practice
- Requirement
- An effective exercise program
- Developing high-quality exercise activities.
- Why exercise
- nternal benefits
- Enhancing capability
- Improving coordination and proficiency
- Finding areas in need of program improvement
- Validating existing plans and procedures
- Externally-driven
- Meeting regulatory requirements
- Responding to political and public pressure
- Demonstrating a commitment to preparedness and meeting expectations
- Philosophy
- alidate capabilities vs. Test
- Training vs. Exercising
- Mix of Exercise Activities
- Exercise Scheduling
- Overall Exercise Cycle
Exercise Scheduling
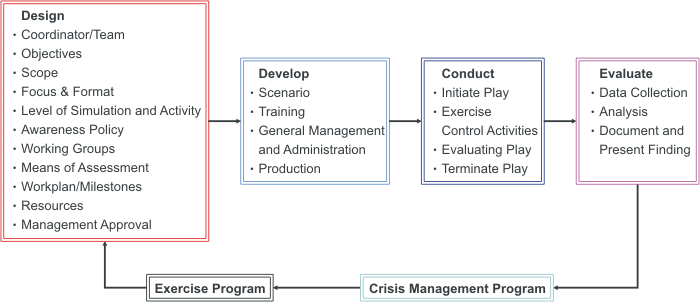
The Exercise Process Cycle
Function of an Management System
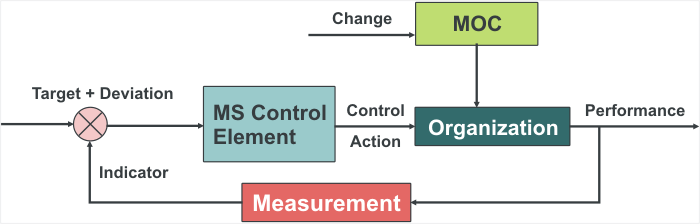
ER Organization
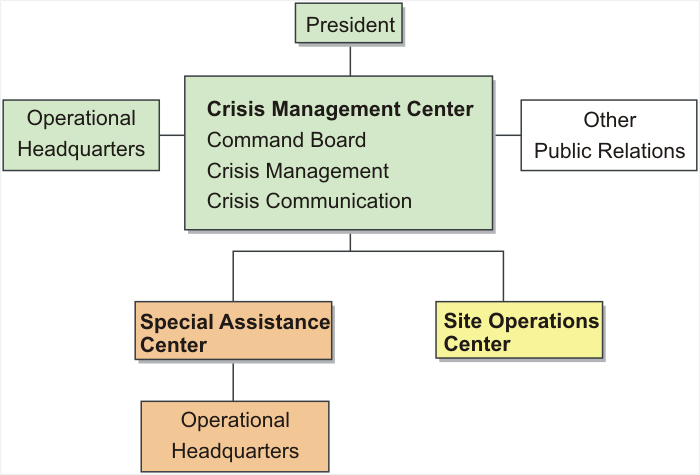
- 3.1 Crisis Response Organizations
Crisis Response Organizations will be established in accordance with Appendix 3A in the event of an emergency.
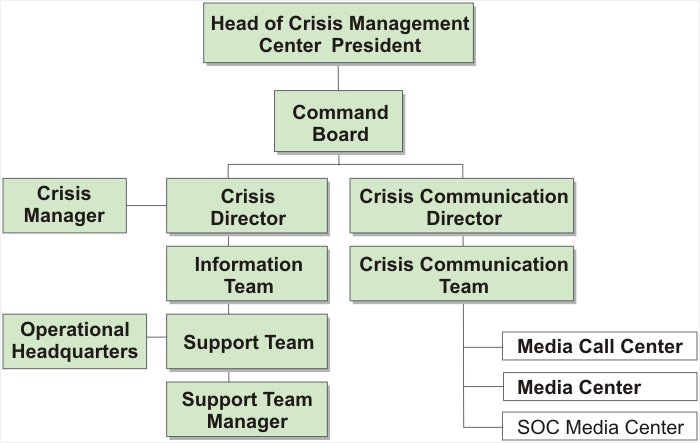
- 3.2 Crisis Management Center
Following organization and staff will be deployed in the CMC.
- Crisis Command Board
- Crisis Director
- Information Team
- Support Team for Departments concerned
- Crisis Communication Director
- Crisis Communication Team
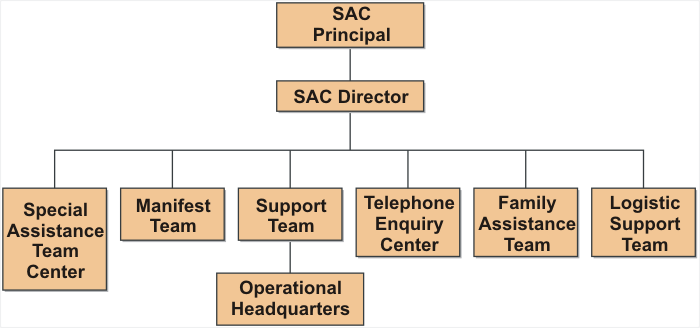
- 3.3 Special Assistance Center
Following organization and staff will be deployed in the SAC.
- SAC Principal
- SAC Director
- Special Assistance Team Center
- Manifest Team
- Support team
- Telephone Enquiry Center
- Family Assistance Team
- Logistic Support Team
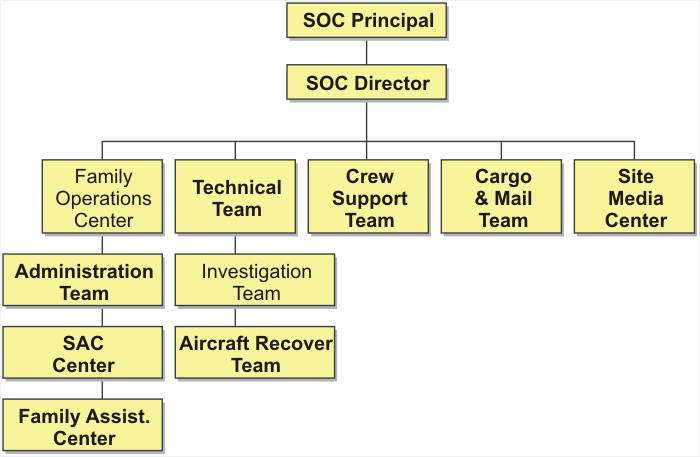
- 3.4 Site Operations Center
Following organization and staff will be deployed in the SOC
- SOC Principal
- SOC Director
- Family Operations Center
- Administration Team
- Special Assistance Team Center
- Family Center
- Technical Team
- Investigation Team
- Aircraft Recovery Team
- Crew Support Team
- Cargo & Mail Team
- Site Media Center
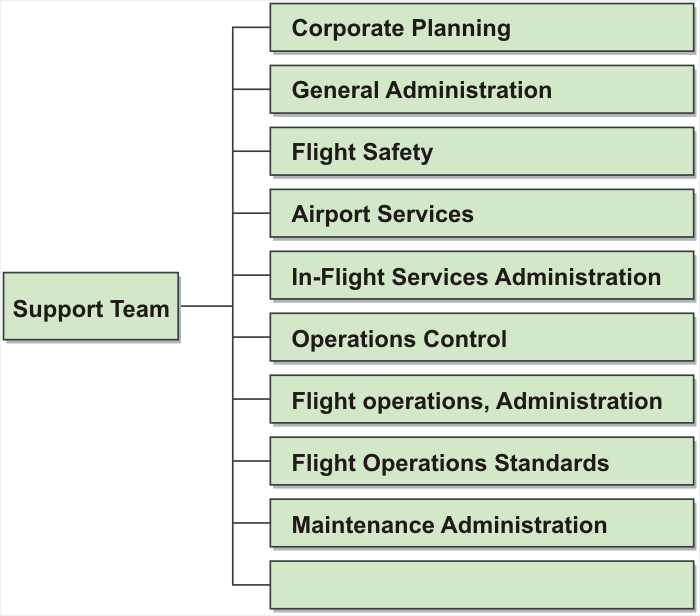
- 3.5 Operational Headquarters and Departments Concerned
- 3.5.1 Department dispatches its staff to the CMC (Appendix 3E)
- Corporate Planning
- General Administration (In charge of Legal Affairs)
- Flight Safety
- Airport & In-Flight Services - Airport Services (In charge of Cargo & Mail Services)
- Airport & In-Flight Services - In-Flight Services Administration
- Operations Control - Administration Group
- Operations Control - Security & Emergency Response Planning Group
- Flight Operations - Administration Office
- Flight Operations - Flight Operations Standards Office
- Maintenance Administration
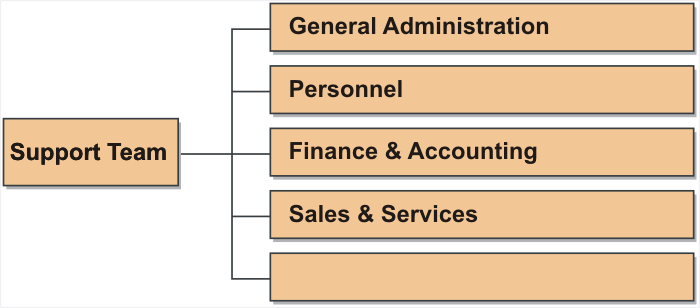
- 3.5.2 Department dispatches its staff to the SAC (Appendix 3F)
- General Administration
- Personnel
- Finance & Accounting
- Sales & Services
- 3.6 List of staff deployment Staff deployment List (Appendix 3G)
- Appendix 3A Organization Chart-General
- Appendix 3B CMC Organization Chart
- Appendix 3C SAC Organization Chart
- Appendix 3D SOC Organization Chart
- Appendix 3E Departments dispatches its staff to CMC
- Appendix 3F Departments dispatches its staff to SAC